One. Experiment Principle
Various tissues of the animal body are taken out from the body, treated with various enzymes (commonly used trypsin), chelating agents (commonly used EDTA) or mechanical methods, dispersed into single cells, and cultured in a suitable medium to make the cells survive, grow and reproduce. This process is called primary culture.
Primary cells retain the important physiological characteristics of many source tissues and can highly mimic the situation in vivo without genetic and chemical changes. Therefore, primary cells have become an ideal cell model in many studies.
Two. Application Introduction
All primary cultured cells from embryos, tissues, organs and peripheral blood prepared by special isolation methods are called primary cells. The cells obtained by primary isolation have similar biological characteristics to those in vivo, and are ideal materials for the study of biological related life activities.
Three. Experiment Methods
(1) Separation method of suspension cells
If the tissue material comes from the suspension material of blood, amniotic fluid, pleural fluid or ascites, low-speed centrifugation can be used. After centrifugation, due to the different specific gravity of various cells, different layers can be formed in the stratification solution, so that the target cells can be obtained according to needs.
(2) Separation method of solid tissue materials
For solid tissue materials, their intercellular connection is tight, in order to fully disperse the cells in the tissue and form cell suspension, mechanical dispersion method (physical lysis) and digestion and separation method can be used. Among them, the mechanical dispersion method is simple and fast, but it has great mechanical damage to tissue and poor cell dispersion effect. It is suitable for dealing with soft tissue with less fiber composition. Digestion and separation method refers to cutting the tissue into small clumps (or paste), further loosening the bridging structure between cells by the biochemical action of enzyme and non enzymatic chemical action, making the clumps bulky and turn into flocculent form. At this time, mechanical method is adopted, and the cell clumps can be fully dispersed by blowing and dispersing with straw, electromagnetic stirring or shaking in a shaking flask to make a small number of cell clusters and a large number of cell suspensions of single cells. After inoculation and culture, the cells are easy to adhere to the wall and grow.
(3) Primary culture of mouse hepatocytes
1. Take the liver: cut off the neck of the mouse to death and take the liver;
2. Remove sundries: remove fat, connective tissue, blood and other sundries;
3. Grind liver: cut the organ into small pieces with surgical scissors and grind them;
4. Trypsin digestion: add trypsin to digest the liver to separate cells;
5. Filter to remove impurities: filter with filter screen to remove large tissue blocks;
6. Count the cells: count by blood cell counting board.
Four. Samples Delivery Requirements
Sample type | Sample requirements | Preservation conditions | Delivery conditions | Note |
Frozen cell | 1. Take the cells in logarithmic growth stage, digest and centrifuge to collect the cells, add the cryopreservation solution, blow and mix well, put it into the cryopreservation tube, mark the cell name/cell algebra, and the number of frozen cells is 1-5*106 / ml 2. After the start of the project, the cells will be resuscitated. Report the cell status 3 days after resuscitation, report the cell contamination 3 to 5 days later and report the mycoplasma contamination 5 tp 7 days later. 3. Cell details (name, culture medium and other culture conditions, etc. if it has been specially treated, it is necessary to inform and provide necessary information) | In liquid nitrogen | With dry ice | All samples need to be uniquely marked and the markings are clearly identifiable |
Resuscitated cell | 1. Use T25 culture bottle for transportation. When the confluence of cells reaches more than 60%, fill the bottle with culture medium, leave only bubbles of button size, seal the bottle with sealing film, mark the cell name/cell Algebra/ inoculation time/medium type, and transport in bottle stably. 2. Report the cell status 3 days after receiving, report the cell contamination 3 to 5 days later and report the mycoplasma contamination 5 tp 7 days later. 3. Cell details (name, culture medium and other culture conditions, etc. if it has been specially treated, it is necessary to inform and provide necessary information) | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Plasmid | 1. High purity, no endotoxin, no protein, genomic DNA / RNA pollution, the ratio of plasmid A260:A280 is between 1.8-2.0 2. The concentration is not less than 0.5 μg/μl, the total amount is more than 100 μg, and there is no endotoxin treatment 3. Carrier details, including name, band, resistance, fluorescent labeling | At - 20℃ | With ice bag | |
Virus | 1. Lentivirus: the titer is not less than 1*108 TU/ml, the volume is about 200 μl, the preparation time is indicated, and there is no repeated freezing and thawing 2. Adenovirus: the titer is not less than 1*109 PFU/ml, the volume is about 200 μl, the preparation time is indicated, and there is no repeated freezing and thawing 3. To determine whether to express fluorescent label protein and its type, it is best to provide virus vector map | At - 80℃ | With dry ice |
Five. Case Display
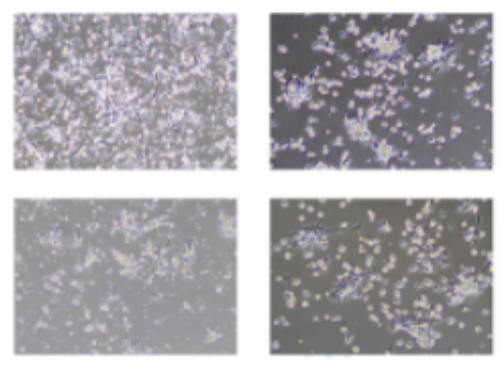
Six. Common Problems
(1) For the selection of primary culture materials, try to select tissues with strong reproductive ability, such as embryos, young organisms or tumor tissues.
(2) Pay attention to aseptic operation. Its operation requirements should be higher than those of surgery
(3) The whole sampling operation should be rapid and the time should not be too long to ensure the activity of embryonic cells.
(4) When using digestion method, the temperature of trypsin should be lower than 37 ℃, and the concentration is only half of that of normally digesting cells. Because this process needs at least 20 min instead of 1~10 min as that of digesting cultured cells. The cells digested first continue to digest in this trypsin digestive solution for more than 10min. Therefore, trypsin cannot act too strongly, otherwise these cells are easy to be damaged.
(5) If the tissue block method is used, the tissue block should be slightly dry and can adhere to the bottle wall before contacting with the culture medium and prevent the tissue block from floating up. If the tissue block does not adhere to the wall, the cells are not easy to grow. Even if the cells grow, they cannot be collected because they cannot be observed due to not being attached to the bottle wall.
(6) During the primary culture operation, DMEM or PBS without serum can also be used to wash uterus, embryo or tissue block.
Seven. Service Process