One. Experiment Principle
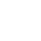
Cell adhesion is not only the basic condition to maintain the stability of tissue structure, but also the regulatory factor of cell movement and function, and has an important impact on cell proliferation and differentiation. Generally, it can be divided into two categories: cell-cell adhesion and cell-matrix adhesion. Many cells in the body, such as epithelial cells, need to be firmly fixed somewhere to function; Other cells, such as white blood cells, are active and need to constantly regulate cell adhesion. The change of cell adhesion also plays an important role in the process of tumor metastasis. Malignant tumors have the ability to separate from primary tumors and spread in vivo, suggesting that these cells have changed in the mechanism of mutual recognition and adhesion.
Two. Application Introduction
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a kind of glycoproteins on membrane surface. They mediate the contact and binding between cells and cells and between cells and extracellular matrix in the way of ligand-receptor specific binding, and regulate cell function. In many physiological and pathological processes such as embryonic development and differentiation, maintenance of normal tissue structure, inflammatory response, immune response, coagulation and thrombosis, wound repair, tumor invasion and metastasis, it plays an important biological role .
Cell adhesion experiments are usually divided into two categories: cell to cell adhesion and cell to matrix adhesion. Many cells in the body, such as epithelial cells, are fixed somewhere to function; Other cells, such as white blood cells, are active and need to constantly regulate cell adhesion. The change of cell adhesion also plays an important role in the process of tumor metastasis. Malignant tumors have the ability to separate from primary tumors and spread in vivo, suggesting that the mutual recognition and adhesion mechanism of these cells have changed. The experiments that need to determine cell adhesion include: mechanical method to determine cell adhesion, radioactive nuclide method to determine cell adhesion, cell separation experiment and tumor cell aggregate formation experiment.
Three. Experiment Methods
1. Add 4.5 × 105 Hep3B cells/well to passage in sterile 6-well culture plates.
2. After 24 hours of culture, transfect 37lrp siRNA into Hep3B cells with Lipofectamine TM 2000 (two parallel wells. See method 7 for specific operation of Lipofectamine TM 2000 transfection). The transfected cells are cultured in 37 ℃ and 5% CO2 incubator, and collect the cells after 48 hours. At the same time, cells with two parallel wells individually are transfected with negative control and no transfection. The final transfection concentration, which is the final siRNA concentration, is 100 nmol / L.
3. Collect the cells after 48 hours of culture, and digest the adherent cells which is cultured with 0.25% trypsin (about 1 × 106) from the wall and make into single cell suspension.
4. Prepared matrigel into 10ug / 250ul (1:300) artificial basement membrane gel with serum-free MEM medium for standby.
5. The 96 hole plate is paved with Matrigel 2ug/50ul in each hole and placed in the Clean Bench for air drying overnight.
6. Add an appropriate amount of serum-free MEM cell culture medium (or PBS or normal saline) into each well of 96 well plate, place it for 60-90 minutes, and wash off the excess gel;
7. Take the transfected, negative control transfected and non transfected Hep3B cells as 4 × 103 / well: inoculate in 96 well plate covered with gel, set three repeat holes, and put them into 37 ℃ and 5% CO2 incubator for 20 min, 40 min and 60 min respectively.
8. Take out the 96 well plate at the corresponding time point, suck out the culture medium, wash it with PBS for 3 times, and wash away the non adherent cells.
9. Add 100 ul methanol into each hole and fix for 15min.
10. Add 100 ul Giemsa staining solution into each well, stain for 15min, and wash the staining solution with distilled water.
11. Count the number of adherent cells under a 200X microscope (8 visual fields per well at a fixed position)
Four. Samples Delivering Requirements
Sample type | Sample requirements | Preservation conditions | Delivery conditions | Note |
Frozen cell | 1. Take the cells in logarithmic growth stage, digest and centrifuge to collect the cells, add the cryopreservation solution, blow and mix well, put it into the cryopreservation tube, mark the cell name/cell algebra, and the number of frozen cells is 1-5*106 / ml 2. After the start of the project, the cells will be resuscitated. Report the cell status 3 days after resuscitation, report the cell contamination 3 to 5 days later and report the mycoplasma contamination 5 tp 7 days later. 3. Cell details (name, culture medium and other culture conditions, etc. if it has been specially treated, it is necessary to inform and provide necessary information) | In liquid nitrogen | With dry ice | All samples need to be uniquely marked and the markings are clearly identifiable |
Resuscitated cell | 1. Use T25 culture bottle for transportation. When the confluence of cells reaches more than 60%, fill the bottle with culture medium, leave only bubbles of button size, seal the bottle with sealing film, mark the cell name/cell Algebra/ inoculation time/medium type, and transport in bottle stably. 2. Report the cell status 3 days after receiving, report the cell contamination 3 to 5 days later and report the mycoplasma contamination 5 tp 7 days later. 3. Cell details (name, culture medium and other culture conditions, etc. if it has been specially treated, it is necessary to inform and provide necessary information) | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Plasmid | 1. High purity, no endotoxin, no protein, genomic DNA / RNA pollution, the ratio of plasmid A260:A280 is between 1.8-2.0 2. The concentration is not less than 0.5 μg/μl, the total amount is more than 100 μg, and there is no endotoxin treatment 3. Carrier details, including name, band, resistance, fluorescent labeling | At - 20℃ | With ice bag | |
Virus | 1. Lentivirus: the titer is not less than 1*108 TU/ml, the volume is about 200 μl, the preparation time is indicated, and there is no repeated freezing and thawing 2. Adenovirus: the titer is not less than 1*109 PFU/ml, the volume is about 200 μl, the preparation time is indicated, and there is no repeated freezing and thawing 3. To determine whether to express fluorescent label protein and its type, it is best to provide virus vector map | At - 80℃ | With dry ice |
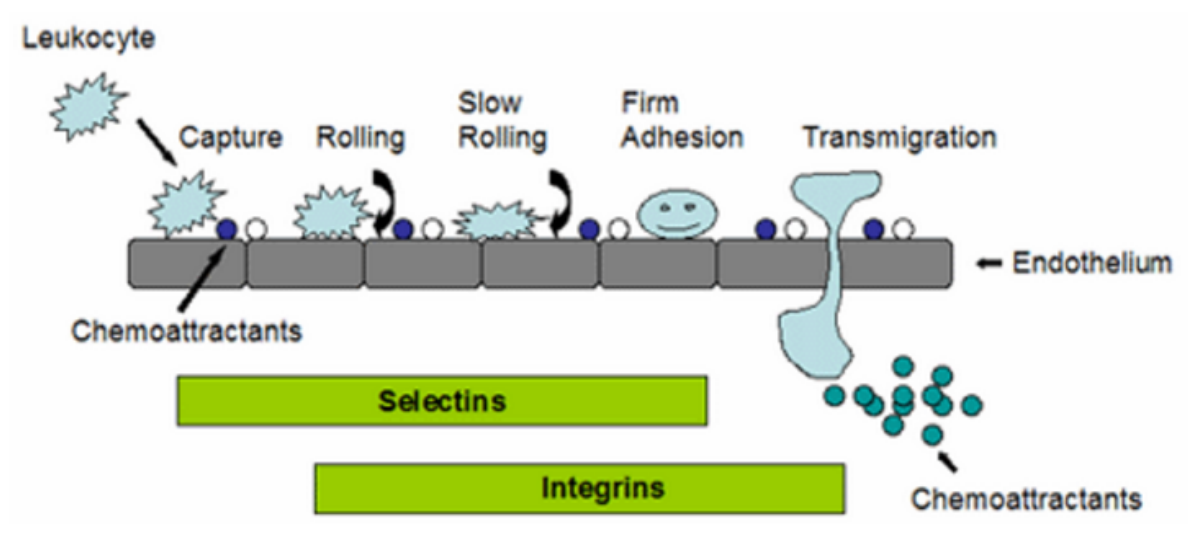
Five. Case Display
Six. Common Problems
1. Cell treatment requires careful operation to avoid artificial damage to cells. The centrifugal force should be as small as possible without losing cells. The action of suspending cells should be gentle to avoid repeated fierce blows, and should not use andvortex oscillator.
2. The staining culture time varies according to the type of cells and the number of cells in each well. In general, leukocytes are difficult to stain, so they need a long culture time. The culture time is generally 1-4 hours, but it can be taken out for visual observation after about 30 minutes.
3. Degree of staining (depending on the type of cell, you need to explore the conditions). When a standard 96 well plate is used, the minimum inoculation amount of adherent cells is at least 1000 / well (100) μl medium). The sensitivity of leukocyte detection is relatively low, so the recommended inoculation amount is not less than 2500 / well (100) μl) medium. If you want to use 24 well plate or 6 well plate for experiment, please calculate the corresponding inoculation amount of each well first, and add staining solution B according to 10% of the total volume of culture medium per well.
4. If possible, multi-channel pipette is recommended to reduce the difference between parallel holes. When adding staining solution B reagent, it is recommended to add it obliquely against the wall of the culture plate and do not insert it under the liquid level of the culture medium, otherwise it is easy to produce bubbles and interfere with the OD value reading. The OD value can be between 0.4-2.0, and the maximum value should be controlled at about 1.0. If it is less than 0.4 or greater than 2.0, please adjust the inoculation amount and culture time.
Seven. Service Process