One. Nude-Mouse Transplanted Tumor Model
(1) Experiment Principle
Transplanting human tumor into immune deficient animals (nude mice) can maintain its biological characteristics, which is very helpful to study the sensitivity of human tumor to drugs. The early work is to transplant human tumors into special parts of animals that lack immune function, such as chicken embryo, animal anterior chamber, hamster cheek pouch, etc. Although there is a certain proportion of survival rate, due to the slow growth of tumors and the limitation of the transplanted part capsule, the tumors are often small and difficult to passage culture, and can not adapt to the experimental treatment that needs more tumor sources. Therefore, using nude mice to establish tumor models for prevention and treatment research is an important topic in basic medical research.
(2) Application Introduction
Subcutaneous tumor bearing in nude mice refers to the experiment of injecting human or mouse derived cells into the subcutaneous of immunodeficient Balb/c nude mice to verify the tumor forming or metastasis ability of cells by applying drugs or other conditions. Nude-Mouse transplanted tumor model is the basis for the study of oncology, immunology, safety evaluation and effectiveness screening of drugs and biological products.
(3) Experiment Method
Step1: prepare cell samples and resuspend with normal saline: disinfect the inoculation environment, resuspend the cells with syringe, disinfect the injection site of nude mice with alcohol cotton ball, and take the cells in logarithmic growth period to make a cell suspension with a concentration of 1*107/ml.
Step 2: cell count, inject cells into the subcutaneous of nude mice: inoculate according to groups, and each nude mouse slowly inoculates 150μl cell suspension under the right axillary skin. After pulling out the needle, quickly gather the cells with the needle to prevent cell fluid leakage.
Step 3: observe and record the tumorigenesis.
Step 4: kill the nude mice and take out the tumor for further research.
(4) Case Display Dispaly

(5) Common Problems
① The cell state has a great impact on tumor formation. When planning the tumor bearing experiment, be sure to ensure that the cells are in a good state. Generally, the number of injected cells is not less than 1*106.
② Although nude mice have certain immune deficiency, it does not mean that there is no rejection reaction at all. Generally, nude mice no more than 7 weeks old are selected for experiments. Too old may affect the effect of tumor formation.
③ The choice of injection site also requires certain skills. Generally, the axillary position of nude mice is selected for injection because this position has rich blood flow and is easy to form tumors in a short time.
④ It is suggested that pre experiments should be carried out before formal experiments to determine the tumorigenicity of cells.
Two. Chronic Depression / EAE Animal Model
(1) Experiment Principle
Depression is a mental illness with depression, slow thinking and slow behavior as the main symptoms. At the same time, it can be accompanied by sleep loss and weight loss.
Model making:
Chronic mild unpredictable stress (CMS) was founded by Katz et al in 1981, but it has many disadvantages, such as too strong stress stimulation often leads to animal death. After the improvement made by Willner et al, it is now a depression model with more application and research. Rats will experience an unpleasant mild stress every day for 2-4 weeks, including cold water swimming (4 ° C, 5min), electric shock (current intensity 1.0mA, frequency 1 time/min), thermal environment (45 ° C, 5min), day and night reversal, flash stimulation (3 times/min), fasting, water prohibition, tail clamping (1min), etc. Each form of stimulation does not happen for two consecutive days to form a CMS to avoid animals adapting to the same stimulation.
(2) Application Introduction
The depression model can be used to screen antidepressants and study the pathophysiological mechanism of depression. Because the stimulating factors used have the similar intensity as the stress events experienced by people in life, it can better simulate the core symptoms of human lack of pleasure and reduced interest, and the model is stable and long-lasting. It is ideal as a depression stress model.
(3) Experiment Method
Adaptive feeding
The experimental mice are kept free to drink and eat at a temperature of 23 ~ 25 ℃, and the animal room is 12g-12h alternating day and night. The experiment will start after one week of adaptive feeding.
EAE modeling
Weigh the experimental mice, anesthetize them with intraperitoneal injection of 3.5% chloral hydrate (0.5ml / 100g), prepare skin on the back, disinfect with alcohol cotton balls, inject each mouse with 0.2ml of antigen emulsion (MOG35-55) subcutaneously at 4 points on both sides of the midline of the back. On the day of immunization (day 0) and 48h later (day 2), inject 500ng (0.2ml) PTX intraperitoneally into the mice in each group. Induce the mice to generate EAE.
(4) Case Display

(5) Common problems
At present, there is no recognized classic test to measure depression. In various depression model animals, the depression level is mainly measured through the following tests: the behavior evaluation is carried out with open-field box test, which shows that the spontaneous exploring behavior of rats is significantly weakened and the exercise ability is reduced. And there are weight loss, decreased sexual behavior, increased plasma glucocorticoid, and disturbed sleep cycle. At the same time, it is found that the rats' natural preference for sugar water decreased. The sugar water consumption test is used to determine the amount of drinking 1% sucrose solution for 24 hours. If the sugar water consumption decreased significantly, it indicates that the depression model is successfully established.
Three. Rats Myocardial Infarction/Spinal Cord Injury Model
(1) Experiment Principle
SD rat myocardial infarction model
The myocardial infarction model is made by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD).
Experimental animal model of rat spinal cord injury
There are many kinds of spinal cord injury models, each of which has its advantages and disadvantages. In application, we should make a scientific choice according to the specific experimental research purpose and conditions. At present, the most commonly used animals for experimental research on spinal cord injury in China are rats, rabbits, cats and dogs. Large animals have the following adverse factors in the actual experimental operation: the surgical operation steps are relatively complex, the incision is easy to be infected, and they are easy to die of postoperative spinal cord injury complications, which affects the experimental results to a certain extent. As a cheap and easy to raise animal, rats have the following characteristics as a model of spinal cord injury: good reproducibility; Good clinical relevance; High homology with human; Strong repeatability; Wide application range; Simple operation; Low mortality.
(2) Application Introduction
SD rat myocardial infarction model
The standardized myocardial model established in the experiment can be further used in the study of ventricular remodeling mechanism and treatment, and even play an important role in the mutual reference and reference of various related fields.
Experimental animal model of rat spinal cord injury
The treatment of spinal cord injury is a major clinical problem. Establishing a good animal model is very important for the study of this disease. The repair and regeneration of spinal cord injury has become the focus of research. Only by establishing a standard and reproducible animal model can we further study the treatment.
(3) Experiment Method
Preparation process of SD rat myocardial infarction model
Weigh the experimental rats and anesthetize them with intraperitoneal injection of 7% chloral hydrate at 5ml/kg. Prepare the skin on the neck and chest, disinfect the operation area with alcohol cotton ball, make a median incision on the neck, make blunt separation of the muscles on both sides to expose the trachea, connect a small animal ventilator after endotracheal intubation in the rat's mouth, make a transverse incision between the 3rd and 4th ribs in front of the left chest after maintaining stable breathing, make blunt separation of each layer of muscles in turn, carefully cut the intercostal muscles, tear the pericardium after exposing the heart, and squeeze out the heart 1-2mm below the right edge of the left atrial appendage at the left edge of the pulmonary artery cone, use a round needle to pass through the myocardial surface below the anterior descending branch of the left coronary artery and ligate it with 5-0 thread. After successful ligation, it can be observed that the ventricular wall below the ligated vessel is slightly white. Immediately put the heart into the chest cavity and suture the chest cavity. Use a syringe to extract the air from the chest cavity. After confirming that there is no open pneumothorax, suture each layer of tissue of the chest wall in turn. After the spontaneous breathing of the rat recovers, remove the endotracheal intubation.
Preparation process of experimental animal model of rat spinal cord injury
The rats are kept free to drink and eat at 23-25 ℃ for 12h-12h alternating day and night in the animal room after purchase, and start the experiment after one week adaptive feeding.
Weigh the Wistar rats and anesthetize them with intraperitoneal injection of 7% chloral hydrate 5ml / kg. Fix them on the operating table in the prone position. Prepare skin with T10 spinous process as the center. After alcohol disinfection, take about 2 cm of the median incision on the back and cut the skin and subcutaneous tissue in turn, and then cut and separat the muscles and fascia on both sides of the spine to expose the spinous process and lamina of T9 ~ T11 vertebral body. Then carefully bite off T10 and nearby spinous process and lamina with hemostatic forceps to expose the dura mater and and maintain its integrity. Use 2.2 × 5mm curved surface to contact with the spinal cord, and compress it with 50g weight for 5min. The paralysis of both hind limbs proves that the modeling is successful. At last, suture the muscle and skin layer by layer.
(4) Case Display

(5) Common Problems
① Equipment: Animal ventilator. It is very important to maintain breathing when making myocardial infarction model by thoracotomy. Although it is said that some experienced people can do it without a ventilator, I think it is the result of experience, and it must be used at the beginning; Besides, I suppose people who need this explanation is not as good as this. Of course, if you have enough money and you don't care about the death of thousands of rats, you can do it without a ventilator. The most important part of micro instruments is needle holding. The thorax and heart of rats are very small, and conventional instruments cannot enter the thorax for suture. Other surgical instruments are mainly ophthalmic instruments.
② Animals: adult healthy rats with good tolerance should be selected. The most important thing is to make full use of every animal, including dead rats. Many people know that making rat models requires more practice, but it doesn’t mean buying a large number of rats, keeping sewing and binding, and then keep throwing away the dead rats; Of course, the death of some mice is normal when making a model of myocardial infarction. The premise of practice is to be familiar with the anatomy and operation process of rats. If possible, it is best to find an anatomical map of rats and be familiar with the anatomical structure of the operation area; At the same time, study the experimental process and be familiar with each experimental step. After the rat dies, don't throw it away in a hurry. Use it to practice every operation step you are not familiar with until you are proficient.
③ Experimenter: the experimenter must have a peaceful and tolerant attitude towards loneliness. Making the model, especially in the early stage, takes time and requires patience and careful exploration. Each step must be carefully studied. The most skilled producer also needs 30 to 40 minutes to make a rat model. Plus the time for preparation and finishing, it takes a day to make ten models. If you forget to eat and sleep and work hard, you may achieve about 15 models. In this way, feeling exhausted is inevitable. How long can you persist? If you are not proficient, it will take two or three hours in preparing one model; At the same time, it's very worrying to watch the rat die in your hand. Therefore, the experimenter must have a good attitude. Those who are eager for success and can't bear loneliness are not suitable for this experiment.
The model is made by tracheotomy, intubation and suture of LAD. There are also models made by oral intubation and liquid nitrogen freezing.
Four. Rat Model of Acute Pancreatitis/Colitis
(1) Experiment Principle
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a very common clinical disease, which is caused by immune disorder. Most patients come from bile duct disease or excessive alcohol intake. Clinicopathological manifestations vary with the severity of the disease, from mild and self limiting disease forms to severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) complicated with sepsis and multiple organ attenuation, resulting in a mortality rate of up to 30-40%. At present, its pathogenesis has not been fully clarified, and there is a lack of effective means to prevent the occurrence and development of pancreatic tissue necrosis.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic nonspecific inflammation mainly involving rectum and colon mucosa. Its main clinical manifestations are abdominal pain, diarrhea, mucus and bloody stool.
(2) Application Introdcution
Acute Pancreatitis
Establish the animal model closest to human pathogenesis in clinical research, so as to understand and explore the pathogenesis, and provide the most important data support for verifying the feasibility of treatment methods and therapeutic drugs.
Ulcerative Colitis
Establishing an animal model similar to human UC has important application value for studying the pathogenesis, pathological development and clinical treatment of UC.
(3) Experiment Method
Acute pancreatitis modeling
The rats are kept free to drink and eat at 23-25 ℃ for 12h-12h alternating day and night in the animal room after purchase, and start the experiment after one week adaptive feeding.
Weigh the Wistar rats and anesthetize them with intraperitoneal injection of 7% chloral hydrate 5ml / kg. Fix them in the supine position and entered the abdominal cavity through the median incision; Find the junction of stomach and duodenum, and then find the opening of biliary pancreatic duct and duodenum downward; Insert a 1ml syringe into the opening of the biliopancreatic duct in the duodenal mucosa and deep into 1cm; Temporarily clamp the hilar part of the biliopancreatic duct and the puncture needle with two arterial clamps to prevent the liquid from flowing into the liver and duodenum when sodium deoxycholate is injected; Inject 1.5% sodium deoxycholate into the biliopancreatic duct at a uniform speed (dosage 1.0ml/kg, injection speed 0.2ml/min); After the injection, continue to block the upper and lower ends of the biliopancreatic duct for 5 minutes, and remove the arterial clamp clamped at the upper and lower ends of the biliopancreatic duct; Supplement ascites and close the abdomen in two layers.
Construction of rat model of ulcerative colitis
The rats are kept free to drink and eat at 23-25 ℃ for 12h-12h alternating day and night in the animal room after purchase, and start the experiment after one week adaptive feeding.
The model rats drink freely with 200g/L honey water, and be given lard by gavage according to their body weight on the next day (the gavage dose is 15g/kg, which is heated and melted before gavage), Baijiu (20ml/kg by gavage) is given together with lard every other day for a total of 20 days. On the 6th and 20th days, 1ml antigen emulsion (containing 8mg antigen) is injected into the left and right plantar, groin and back of rats. Rats in each group are fasted for 36 hours on the 21st day, anesthetized with 7% chloral hydrate (5ml / kg), gently inserted the silicone tubein to the anus for 8-10cm, the normal control group is enema with 2.5ml normal saline, and the model group us enema with enema solution at the dose of 2.5ml/animal (lift the tail of rats after enema and invert it for 1min).
(4) Case Display
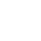
(5) Common Problems
① No expected effect or high mortality in animals: the drug dose needs to be controlled
② The model constructed in general laboratory is acute pancreatitis model, which is not suitable for long-term administration experiment.
Five. Rat Brain Injury / MCAO Model
(1) Experience Principle
Rat MCAO Model
MCAO is the middle cerebral artery occlusion. This model blocks the external carotid artery and its branches, and blocks the pterygopalatine artery to cut off the lateral collateral circulation blood flow of extracranial sources. The middle cerebral artery ischemia model is established by mechanically blocking the blood supply of the origin of the middle cerebral artery by e a suture from the external carotid artery to the anterior cerebral artery through the internal carotid artery
Brain injury in rats
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the main lethal and disabling factors in the world. It causes the disorder of neurological function through a series of changes of neurochemical molecules and signals, resulting in the damage of behavior, cognition and memory.
(2) Application Introduction
Rat MCAO model
Stroke, also known as "cerebrovascular accident", is an acute cerebrovascular disease, including ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, in which ischemic cerebrovascular disease accounts for 60-70%.
Stroke, also known as middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), is a focal cerebral ischemia model. At present, it is the most widely used cerebral ischemia model. Its pathogenesis is similar to that of human ischemic stroke, which is of great significance for making a simulated human cerebral ischemia model and for the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia and drug screening.
Brain injury in rats
Although a lot of human and financial resources have been invested in the research of TBI, there is no effective treatment scheme due to its complex pathophysiological mechanism. How to improve the survival rate of these patients is of great significance to our clinical work.
(3) Experiment Method
Animal adaptive feeding
The animals are kept in the animal room for 12h-12h day and night after purchase, and the animals are kept free to drink and eat at a temperature of 23-25 ℃, and start the experiment after one week adaptive feeding.
Construction of Rat MCAO Model
The MCAO model of rats is established according to the modified Zea longa suture method. Rats fast 12 hours before operation and are allowed to drink.
Weigh the rats, anesthetize them with intraperitoneal injection of 7% chloral hydrate (0.5ml / 100g), prepare the anterior part of the neck and disinfect it, perform the median neck incision, make a blunt separation over the right subcutaneous tissue and muscle to expose the common carotid artery. Use ophthalmic forceps to carefully separated the vagus nerve and periarterial mucosal tissue accompanying the common carotid artery, and separate the common carotid artery by about 1 ~ 1.5cm. Continue to separate to the head and carefully remove the mucosal tissue covering the artery. It can be seen that the external carotid artery, internal carotid artery and common carotid artery are distributed in a "Y-shape", and independent internal and external carotid arteries are separated. Ligate the external carotid artery and the proximal end of the common carotid artery, embed suture in the internal carotid artery and temporarily clamp with an artery clamp. Cut a "V" shaped incision at the ligation of the proximal end of the common carotid artery, clamp the tether with ophthalmic forceps, and enter the internal carotid artery from the common carotid artery. When reaching the artery clamp, tighten the embedded line slightly (to prevent blood seepage), loosen the artery clamp and continue to insert the suture. When the black mark of the special suture reaches near the Y-shaped bifurcation, the suture has entered the middle cerebral artery and cannot continue to move forward.
Testing
After the suture is inserted, tighten and fix the reserved ligature wire. Clean the blood clot in the neck with medical cotton swab, suture the skin, disinfect with alcohol cotton ball, and put the rats back into the cage. After 90 minutes, anesthetize the rats, disinfect the neck, open a small opening, clamp the fixed part of the suture with ophthalmic forceps, pull out the suture by about 1cm to realize blood flow reperfusion, cut off the excess suture and suture layer by layer.
SD Rat Brain Injury Model (Feeney free fall method)
Weigh the rats, anesthetize them with 7% chloral hydrate (5ml / kg), prepare skin on the head, prone and fixe on the craniocerebral injury instrument. After the disinfection of the operation area with alcohol cotton ball, cut put the skin on the top of the rat head and strip the fascia. Taking 3mm in front of the herringbone suture and 3mm on the right side of the coronal suture as the circle center, use the skull drill to drill holes and expand the bone window (diameter 5mm). During the drilling process, pay attention not to damage the dura mater. Gently place the Injury pad on the dura mater in the center of the bone window, and use 40g weight to fall down freely along the sliding rod from 20cm to hit the injury pad (impact force is 800g · cm), resulting in local brain contusion and laceration of the right parietal lobe of rats. Seal the window with bone wax and suture the scalp.
(4) Case Display
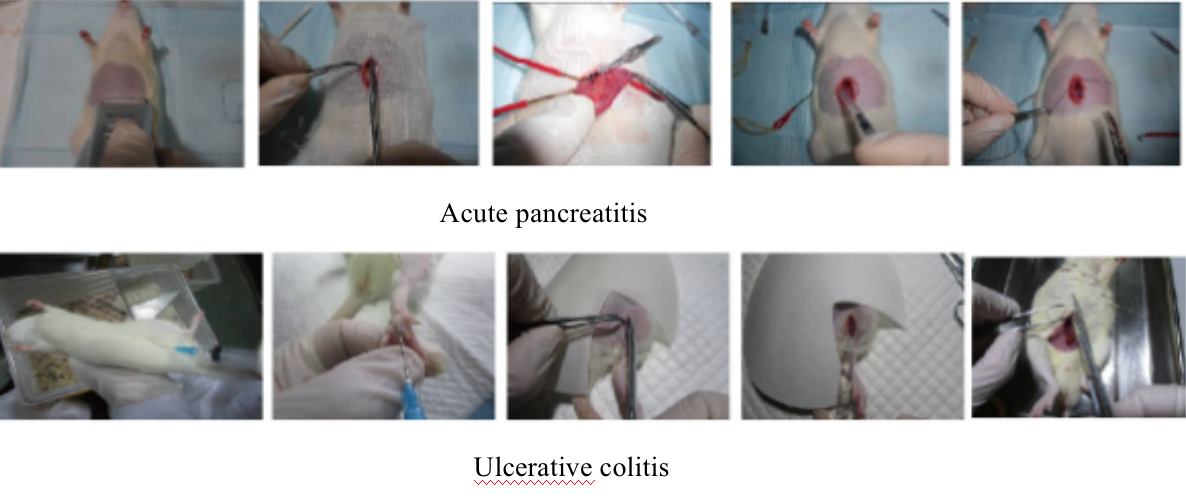
(5) Common Problems
1) When separating neck muscles, small muscles on both sides are called bubbling glands (many people mistakenly think it is thyroid gland) to avoid injury and bleeding.
2) If you see the carotid sheath, pay attention to carefully separate the vagus nerve. If it is damaged, it may affect its breathing and lead to death.
3) When separating the blood vessels, try to peel off the blood vessels as clean as possible, so that when cutting with ophthalmic scissors, the adventitia will not be cut by mistake, and an oblique incision should be cut.
4) Fasten the suture and pay attention to the strength when winding the thin wire at the distal end of CCA. The tying is a must, otherwise there will be more bleeding, but do not tighten it too tightly, otherwise it will be difficult to insert the wire
5) The suture is inserted a little bit by several times until it encounters slight resistance, rather than clamping the middle part of the suture and inserting it all at once.
Six. Atherosclerosis/Pneumonia Model
(1) Experiment Principle
Atherosclerosis Model
There are several common replication methods (including hyperlipidemia model):
① High cholesterol and high fat feed feeding method: it is a commonly used method at present. It is characterized by low mortality and fulfill long term observation, but it takes a long time. Generally, rabbits, pigeons and chickens can produce obvious hyperlipidemia after feeding for several weeks, and early atherosclerotic lesions can be formed after several months while it is difficule for rats, mice and dogs. If egg yolk, cholic acid and lard are added to the feed, the formation will be facilitated . In order to promote the formation of lesions, methylthiouracil, propyl thiouracil, hyperthyroidism, vitamin D and sucrose can also be added to high-fat feed.
② Immunologic method: injecting rat aortic homogenate into rabbits can cause blood cholesterol β- Lipoprotein and triglyceride increased.
③ Injection of catecholamines: it can cause aortic lesions, showing the elongation, splitting or fracture of elastic fibers in the middle layer of vascular wall, necrosis and calcification in the lesions.
④ Injection of homocysteine: it can narrow the coronary artery lumen, proliferate the intimal myocyte, proliferate the fibrous tissue, rupture of elastic fibers, thicken the tube wall, and generate piles of granular and fibrous metachromatic substances in matrix.
⑤ Injection of surfactant: triglyceride increases the most, followed by phospholipids, free fatty acids and free cholesterol, but it has no effect on cholesterol.
⑥ Cholesterol--fat emulsion intravenous injection method: total cholesterol rises to 6 times of normal, mainly free cholesterol, and the ratio of free cholesterol to total cholesterol is 90%. After that, the total plasma cholesterol gradually decreased, and a low peak appeared at 6 hours, and then increased slightly. After 3 ~ 4 days, the ratio of free cholesterol to total cholesterol is close to normal (about 40%), until 7 ~ 14 days later plasma cholesterol returns to normal.
⑦ Neonatal rat method: it is generally believed that this hypercholesterolemia is very sensitive to thyroxine and its derivatives, but insensitive to some cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors.
⑧ Other methods: there are many factors that can induce hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. For example, make animals suffer from cerebral ischemia, electrically stimulate the central nervous system, high stress state, apply high-dose estrogen in birds and expose them to CO, injury of arterial wall endothelial cells by balloon heterotube, etc.
Construction of mouse pneumonia model
Bacterial pneumonia accounts for 80% of all kinds of pathogen pneumonia in adults. However, in the past 30 ~ 40 years, due to the increasing rate of bacterial drug resistance, a large number of broad-spectrum or ultra broad-spectrum antibiotics have been put into clinical practice, which has not continuously reduced the mortality of pneumonia. About 15% of hospitalized deaths have been reported to be related to pneumonia. The mortality of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is 5% ~ 10%, while that of hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP) is as high as 20% ~ 50%.
(2) Application Introduction
Atherosclerosis model
Atherosclerosis (AS) is one of the diseases that seriously endanger human life and health in China and the world. As a cardiovascular disease that seriously affects human health, its incidence rate and mortality are among the top of various diseases. Therefore, it is of great significance to establish a whole animal model of experimental atherosclerosis with lipid metabolism and plaque similar to human.
Construction of mouse pneumonia model
The clinical symptoms of pneumonia tend to be atypical, and the so-called "severe" pneumonia occurs from time to time, especially in infants, the elderly and immunosuppressive patients, the mortality is very high. Improving the level of etiological diagnosis of pneumonia, establishing the animal model of pneumonia, establishing the animal diagnostic standard of pneumonia and the observation index of animal model of pneumonia are urgent to be solved in the clinical treatment of severe pneumonia.
(3) Experiment Method
Atherosclerosis model
There are several common replication methods (including hyperlipidemia model):
① High cholesterol and high fat feeding method: specific replication method:
Rabbit induced model: the rabbit which weighs about 2kg is fed with cholesterol 0.3g every day, and aortic atherosclerotic plaque can be seen by naked eyes after 4 months; If the daily dose is increased to 0.5g, plaque can appear after 3 months; If it is increased to 1g per day, the duration can be reduced to 2 months. Adding 15% egg yolk powder, 0.5% cholesterol and 5% lard to the feed, subtracting the cholesterol in the feed after 3 weeks, and then feeding for 3 weeks, the incidence of aortic plaque can reach 100%, and the serum cholesterol can grow to 2000mg%.
The induced model of rats is fed with 1 ~ 4% cholesterol, 10% lard, 0.2% methylthiouracil and 86 ~ 89% basic diet for 7 ~ 10 days; Or feeding 10% protein yellow powder, 5% lard, 0.5% bile salt and 85% basic feed can form hypercholesterolemia after 7 days.
Rat induced model: male mice are fed with high-fat diet with 1% cholesterol and 10% lard, and the serum cholesterol increased to 343 ± 15mg after 7 days; If 0.3% cholic acid is added to the feed for 7 days, the serum cholesterol can be as high as 530 ± 36mg%.
Chicken and pigeon induced model: a 4 ~ 8 weeks leghorn chicken is fed with 1 ~ 2% cholesterol or 15% egg yolk powder and 5 ~ 10% lard. After 6 ~ 10 weeks, the blood cholesterol increased to 1000 ~ 4000mg, and the incidence of thoracic aortic plaque reached 100%. Pigeons is fed with cholesterol 3g / kg / day and methylthiouracil 0.1g can produce more animal plaques.
② Immunologic methods: injecting rat aortic homogenate into rabbits can cause blood cholesterol β- Lipoprotein and triglyceride increased. Rabbits are injected with horse serum 10ml / kg once for 4 times, with an interval of 17 days. The intimal injury rate is 88%, and there are atherosclerotic lesions in the coronary artery; At the same time, given high cholesterol diet, the lesion is more obvious. Rabbits are fed with 1% cholesterol beverage and intravenous injection of bovine serum albumin 250mg / kg can accelerate the formation of intimal lesions caused by high cholesterol diet.
③ Injection of catecholamines: rabbits are given norepinephrine 1mg / day intravenously for 30 minutes. One method is to drip for 15 minutes, stop for 5 minutes and then drip for 15 minutes; Another method is to drip for 5 minutes and stop for 5 minutes, repeated 6 times.
④ Homocysteine injection method: inject 20 ~ 25mg / kg / day of DL homocysteine thiolactone into rabbit skin (1mg / ml with 5% glucose solution) for successive 20 ~ 25 days, then adult and young rabbits can have typical lesions of atherosclerosis.
⑤ Injection of surfactant: rats are intraperitoneally injected with Triton WR1339 300mg / kg, and the serum cholesterol increases by 3-4 times after 9 hours; After 20 hours, the serum cholesterol of male rats is still 3 ~ 4 times that of normal, while that of female rats is about 6 times; The lipid raising effect reached the highest point about 24 hours after treatment, and returns to normal about 48 hours.
⑥ Intravenous injection of cholesterol--fat emulsion: dissolve 3g of cholesterol and lard under electromagnetic heating and stirring, add tween-803g, mix well, then slowly add 5ml of propylene glycol and boiling water, fully stir and emulsify to 100ml, and check under the microscope after suction filtration. The emulsion particles are uniform and less than 7 ~ 8 μm can be applied. When 5ml/kg is injected intravenously into the ear margin of rabbits, plasma cholesterol and triglyceride increase immediately.
⑦ Neonatal rat method: generally, the serum cholesterol of neonatal rats is 2 ~ 3 times higher than that of adult rats, which is due to the high fat content in milk and the imperfect thyroid function. If milk is replaced by common feed, serum cholesterol will soon drop to the level of normal adult rats. Select young suckling rats born 25 days old, both male and female, weighing 30 ~ 50g to observe the blood cholesterol lowering effect of the drug without leaving the milk of the mother rats, and compare the effect with that of the control group.
⑧ Other methods: there are many factors that can induce hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. For example, make animals suffer from cerebral ischemia, electrically stimulate the central nervous system, high stress state, apply high-dose estrogen in birds and expose them to CO, injury of arterial wall endothelial cells by balloon heterotube, etc.
Construction of mouse pneumonia model
Animal adaptive feeding
C57BL / 6 mice are kept free to drink and eat at a temperature of 23-25 ℃ in the animal room for 12h-12h alternating day and night, and start the experiment after one week adaptive feeding.
Construction of pneumonia model in C57BL / 6 mice
C57BL / 6 mice are anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 7% chloral hydrate (0.5ml / 100g). After successful anesthesia, they are fixed on the operating table in the supine position, prepared skin on the neck, disinfected with alcohol cotton balls, made a median incision on the neck (about 1.5cm), separated the skin and muscle tissue of the neck, exposed the trachea, pierced the needle into the trachea with 1ml syringe, and slowly drip LPS (5mg / ml) solution at 1ml / g. after injection, they were sutured layer by layer and returned to cage.
(4) Case Display

(5) Common Problems
① The atherosclerotic model should be established by high-fat diet combined with mechanical injury of arterial intima. High fat diet precedes balloon injury. The operation should be carried out 7-10 days after feeding high-fat diet, that is, there are high-fat incentives and pathogenic factors of arterial intimal injury.
② The common carotid artery should be separated as clean as possible, otherwise it is easy to cause bleeding due to poor clamping, making it inconvenient to insert the balloon injury tube.
③ After the balloon injury tube reaches the middle of the common carotid artery, the force must be light when repeatedly pulling, so as to prevent the accidental death of animals.
Service Process