A. Experimental Principles
The production of paraffin embedded tissue section includes a series of steps such as fixation, dehydration, clearing, wax dipping, embedding and sectioning. It is a conventional experimental method in morphological disciplines such as histology and pathology.
1) Harvest and dissection of materials: harvest the material according to the purpose and requirements of experiment. And the materials should be representative.
2) Killing and fixing: use drugs to quickly fix cells to maintain its original state and structure.
3) Dehydration: this step is to remove the water in the tissue and convenient for clearing, wax dipping, and embedding.
4) Clearing: the purpose is to remove the dehydrating agent from the material, make the material transparent and increase the refractive index; At the same time, it is convenient for the following steps like wax dipping and embedding.
5) Wax dipping: the purpose is to gradually remove the transparent agent and replace it with embedding agent.
6) Embedding (wax embedding)
7) Trimming: cut the embedded wax into small pieces.
8) Slicing: cut the wax block into continuous wax strips with a slicer.
9) Sticking: stick the qualified slices on the clean slide.
10) Dewaxing, staining, dehydration, clearing and sealing: the slice shoul be dewaxed, stained, re-dehydrated and re-cleared after sticking slides, and then be permanently preserved.
B. Application Introduction
Paraffin embedded section is an important tool for qualitative, localization and quantitative analysis of the morphological structure and chemical substances of organs, tissues and cells.
C. Experimental Methods
1) Collection and division of materials
2) Killing and fixing
3) Dehydration
4) Clearing
5) Wax dipping
6) Embedding (wax embedding, GSB)
7) Trimming
8) Slicing
9) Sticking
10) Dewaxing, staining, dehydration, clearing, and sealing
D Sample delivering requirements
Sample type | Sample requirements | Preservation conditions | Delivery conditions | Note |
Fresh tissue | For the fresh tissue, it should be washed the blood away with PBS and preserve in -80°C immediately | At -80°C | With dry ice | All samples need to be uniquely marked and the markings are clearly identifiable |
Regular fixed tissue | The volum of the regular tissue is within 2cm*2cm*0.5cm in general. Fixation is to keep the original shape of the tissue as much as possible and clean up the blood and excess parts; the volum of fixative fluid should be at least 10 times of the tissue, and the container should be big enough to hold the tissue without squeezing it. The type of fixative fluid and the fixed duration should be marked | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Special fixed tissue | For tissue like testicle, eyeball, spinal cord, muscle, and so on: the correspondent special fixative fluid is recommended for fixation to ensure the fixing effect. | |||
Paraffin embedded tissue | The tissue should be embedded in a standard paraffin embedding cassette, and paraffin wax should be evenly bonded to the tissue with no crack; the thickness of the wax block is determined by the number of slices required, and the effective thickness should be at least 0.1 cm. Provide the paraffin embedded tissue made within six months, otherwise the antigens of the paraffin may be lost and fail to detect the protein when performing immunohistochemistry. | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Tissue section | It needs to pick up the section with anti-drop slides and mark the thickness of the section, and the temperature and duration of baking. The tissue should be near the lower third of the slice | At 4°C | With ice bag | |
Cell climbing sheet | Use the special cell climbing sheet for the orifice plate. After the cell climbing sheet is fixed, wash it with PBS for 2 to 3 times, store it in PBS, and seal the orifice plate with sealing film. Each climbing sheet shall have a unique mark on the orifice plate cover and electronic grouping information to prevent the mark from being blurred during transportation. | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Plant example | Fix the fresh tissue with FAA and its degree of lignification is not high; for thinner blades, if parallel blade slicing is required, it is difficult to ensure complete cutting; the diameter of the rhizome should be larger than 1 mm. | At ambient temperature | At ambient temperature | |
Antibody | There should be clear marks to identify the antigens on the containers and the instructions should be attached. The amount of antigens should be larger than the experiment required. For tissue sections and tissue chips, calculate the amount of antibody according to a section of 100 μl after dilution; for the round coverslips of the 24 well plate cell climbing slide, calculate the amount of antibody according to a section of 100 μl after dilution; for the round coverslips of the 12 well plate cell climbing slide, calculate the amount of antibody according to a section of 400 μl after dilution | At -20°C | With ice bag or dry ice |
E. Case Display

F. Common Problems
1. The slices is rolled or wrinkled
① The angle of slicer is too large or too small, and the adjustment angle should be 5 °.
2. The slices are hollow and broken
① Slice slowly and gently.
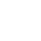
G. Service Process